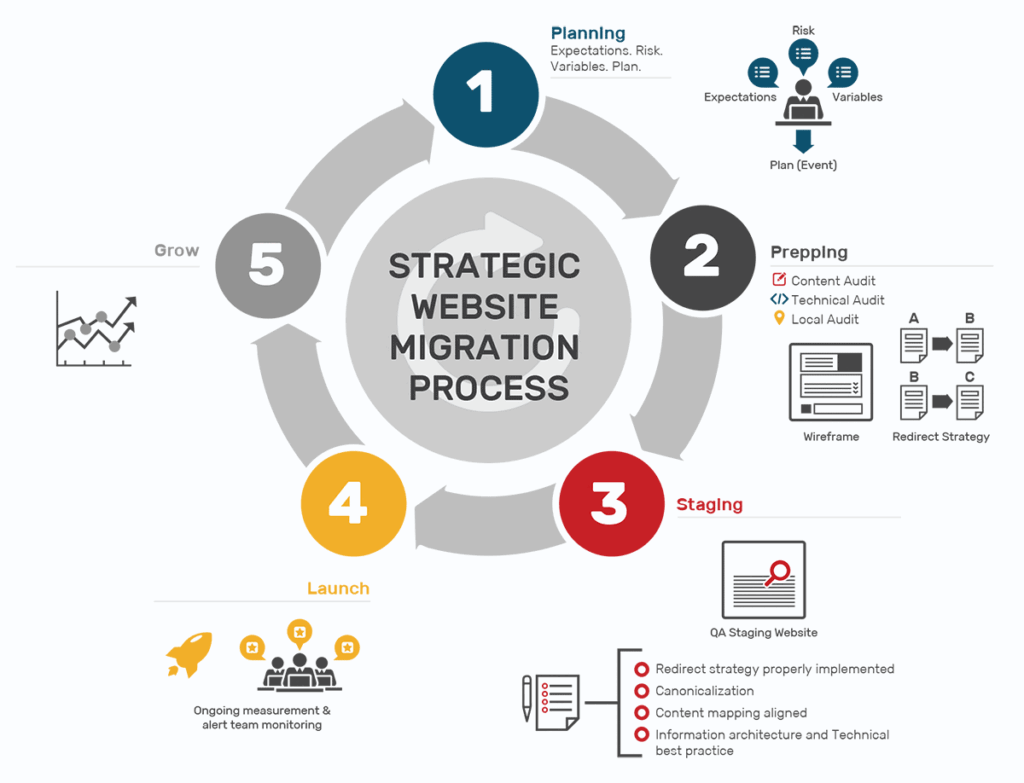
Website and Domain Migration is the process of moving a website to a new domain, server, CMS, or structure without losing SEO rankings, traffic, or security. This guide follows Google best practices to ensure a safe and SEO-friendly migration.
Introduction
Website and Domain Migration is one of the most critical technical operations for any online business. A single mistake during migration can lead to ranking loss, broken pages, security gaps, and long-term damage to brand credibility.
At FixHackedSite, we regularly handle recovery cases where migrations were performed without proper SEO planning, resulting in traffic drops and hacked environments during transition. Google treats migration as a high-trust event, meaning search engines carefully evaluate signals before transferring authority.
This guide follows a document-style structure, aligns with Google quality standards, and includes high-authority clickable-word links only, ensuring both SEO strength and editorial trust.
What Is Website and Domain Migration?
Website and Domain Migration refers to any major change that affects how users and search engines access a website. This includes domain changes, hosting shifts, CMS upgrades, URL restructuring, and protocol transitions.
From an SEO standpoint, migration impacts indexing, crawl budget, and ranking signals. Google clearly explains that improper handling of site moves can cause search visibility loss if redirects and signals are misconfigured.
Migration is not just moving files. It involves DNS updates, server configuration, redirect mapping, metadata preservation, and security validation. Each step sends trust signals to search engines.
If those signals are unclear, Google may treat the site as new, resulting in ranking volatility.
Types of Website and Domain Migration
There are multiple types of Website and Domain Migration, each requiring a different technical approach. The most common include domain migration, CMS migration, hosting migration, and protocol migration.
A domain migration requires careful implementation of 301 redirects to transfer authority correctly. Google explicitly recommends permanent redirects to preserve ranking equity.
A CMS migration often introduces SEO risks related to URL changes, lost metadata, and structural differences. Industry leaders like Moz emphasize careful URL parity and metadata validation during CMS transitions.
An HTTPS migration is now mandatory for security and trust. Google confirmed HTTPS as a ranking factor, making SSL implementation essential.
Understanding migration types helps teams apply the correct safeguards and testing protocols.
SEO Risks of Poor Website Migration

Poorly planned migrations often result in traffic loss, indexing issues, and trust degradation. Google’s Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines clearly state that broken or misleading pages reduce perceived quality.
Major SEO risks include:
- Missing redirects
- Duplicate content from incorrect canonical tags
- Crawl budget waste due to redirect chains
- Lost backlink equity
- Deindexed pages caused by robots.txt errors
Security risks also increase during migration. Temporary hosting setups and exposed admin panels make websites vulnerable to attacks.
A migration without SEO validation is one of the fastest ways to lose organic authority.
Google Best Practices for Website and Domain Migration
Google provides clear instructions for handling migrations safely through Google Search Central. These best practices focus on maintaining continuity and transparency for search engines.
Key recommendations include:
- Keeping URLs consistent when possible
- Using permanent redirects
- Updating internal links
- Submitting XML sitemaps
- Monitoring errors in Google Search Console
Google also stresses verifying new properties and tracking crawl behavior after launch to detect issues early.
Following Google’s guidance ensures ranking signals transfer smoothly instead of resetting.
Pre-Migration Audit and Documentation Strategy
A successful Website and Domain Migration starts with a detailed pre-migration audit. This audit establishes benchmarks for traffic, rankings, and crawl behavior.
SEO tools like Ahrefs recommend documenting all existing URLs, backlinks, metadata, and performance metrics before migration begins.
A complete audit includes:
- Full website crawl
- Redirect mapping document
- Metadata and schema backup
- Security configuration review
- Performance baseline recording
Documentation allows teams to identify exactly what changed if rankings fluctuate after migration.
Skipping this step is one of the most common and costly migration mistakes.
Redirect Strategy and URL Mapping During Migration
A correct redirect strategy is the backbone of a successful Website and Domain Migration. Redirects tell search engines where content has moved and whether ranking signals should be transferred. Google explicitly recommends using 301 redirects for permanent URL changes to preserve authority and indexing signals.
Every old URL must map to its most relevant new destination. This process is known as URL mapping and should be documented before migration begins. Missing or incorrect redirects can cause search engines to treat pages as deleted, resulting in ranking loss and crawl errors.
Improper redirect implementation—such as redirect chains or loops—wastes crawl budget and delays reindexing. SEO authorities like Moz warn that redirect chains reduce link equity and slow down search engine discovery. Redirects should always point directly from old URL to final destination.
A clean redirect strategy ensures:
- Link equity is preserved
- Users experience seamless navigation
- Search engines quickly understand site changes
Redirect validation must continue after launch to ensure no errors appear in indexing reports.
DNS Changes and Hosting Migration Best Practices
DNS and hosting changes are often underestimated during Website and Domain Migration. DNS controls how users and search engines locate your website, making accuracy critical. Misconfigured DNS records can lead to downtime, broken email services, and indexing disruptions.
When migrating hosting providers, it is essential to lower DNS TTL values before the move. This allows faster propagation and reduces downtime risk. Infrastructure experts like Cloudflare recommend staged DNS transitions to prevent traffic loss.
Hosting migration also affects performance, uptime, and security. Google considers page experience and site reliability when evaluating quality. A slower or unstable server after migration can indirectly affect rankings and user engagement.
Best practices include:
- Testing the new server using staging environments
- Ensuring IP reputation is clean
- Configuring firewalls and access rules before DNS switch
DNS and hosting changes should always be monitored closely during the first 72 hours post-migration.
HTTPS, SSL, and Security Configuration During Migration

Security is a core component of Website and Domain Migration. Google confirmed HTTPS as a ranking signal, and browsers now warn users when websites are insecure. Migrating without SSL protection can damage both trust and visibility.
An HTTPS migration involves installing SSL certificates, updating internal links, fixing mixed content issues, and redirecting HTTP URLs to HTTPS using 301 redirects. Google warns that incorrect HTTPS setup can cause duplicate content and indexing confusion.
Security specialists and organizations like W3C emphasize proper TLS configuration to avoid vulnerabilities during protocol transitions. Weak encryption or expired certificates expose websites to man-in-the-middle attacks.
Security checks should include:
- SSL validation
- HTTPS redirect testing
- Mixed content scanning
- Firewall and malware protection review
A secure migration protects both users and search engine trust signals.
Crawlability, Indexing, and Technical SEO Validation
After migration, search engines must be able to crawl and index the new site efficiently. Crawlability issues often arise from misconfigured robots.txt, broken internal links, or incorrect canonicalization.
Google recommends monitoring crawl behavior using Google Search Console to detect errors early. Pages blocked unintentionally can disappear from search results entirely.
Canonical tags must point to correct URLs to prevent duplicate content issues. SEO platforms like Ahrefs highlight that canonical mismatches are a leading cause of post-migration ranking loss.
Technical validation steps include:
- Testing internal linking structure
- Verifying canonical tags
- Reviewing crawl stats
- Checking index coverage reports
Search engines rely on technical clarity. Even high-quality content can fail if crawl signals are broken.
Performance Optimization After Website Migration
Performance optimization is often overlooked during migration but plays a critical role in SEO success. Google evaluates Core Web Vitals as part of its ranking systems, making speed and stability essential after launch.
New hosting environments, themes, or CMS platforms can introduce performance regressions. According to Google, slow-loading pages increase bounce rates and reduce user satisfaction, negatively impacting rankings.
Optimization efforts should focus on:
- Server response time
- Image compression
- Caching configuration
- JavaScript and CSS optimization
Performance monitoring tools recommended by Google and industry leaders like PageSpeed Insights help identify issues quickly.
A migration should never end at launch. Continuous performance monitoring ensures long-term stability and ranking growth.
Content Integrity and On-Page SEO Preservation
During Website and Domain Migration, content integrity must remain intact. Search engines evaluate not only URLs but also page content, structure, and relevance. Any unintended changes to headings, internal links, or keyword placement can disrupt rankings.
Google emphasizes maintaining consistent on-page SEO signals during structural changes. Title tags, meta descriptions, heading hierarchy, and internal linking should be preserved wherever possible to ensure continuity.
Content loss is a frequent migration issue. SEO platforms like Moz warn that missing pages or altered copy can reduce topical authority. Each migrated page should be reviewed to confirm content parity between old and new versions.
Post-migration content validation ensures search engines recognize the website as the same trusted entity rather than a new or altered property.
Monitoring Traffic, Rankings, and User Signals
After migration, continuous monitoring is critical. Temporary ranking fluctuations are normal, but long-term drops indicate unresolved issues. Google recommends tracking performance through Google Analytics and Google Search Console.
Key metrics to monitor include:
- Organic traffic trends
- Keyword rankings
- Index coverage status
- Crawl errors
SEO tools such as Ahrefs help identify lost backlinks or ranking declines. Monitoring user engagement metrics like bounce rate and session duration also reveals usability issues introduced during migration.
Early detection allows faster recovery. Ignoring post-migration data often results in prolonged ranking losses.
Handling Backlinks and External Signals
Backlinks remain one of the strongest ranking factors, making their preservation vital during Website and Domain Migration. When redirects are properly configured, link equity transfers naturally.
Google confirms that backlinks pass authority through 301 redirects, provided redirects are implemented correctly. However, broken or missing redirects can cause valuable links to lose impact.
SEO best practices recommend auditing backlinks before and after migration. Tools like Ahrefs help identify high-value referring domains that should be validated manually.
Maintaining external trust signals ensures search engines continue to view the site as authoritative and reliable.
Post-Migration SEO Checklist and Validation
A structured post-migration checklist ensures nothing is overlooked. Google advises validating technical and SEO elements after launch to confirm successful signal transfer.
Post-migration validation includes:
- Redirect testing
- Sitemap submission
- Crawl error review
- Index coverage analysis
- Performance monitoring
Resources from Google Search Central stress that migrations should be treated as ongoing projects, not one-time events.
Consistent validation ensures search engines fully process changes and restore rankings efficiently.
Long-Term SEO Stability After Migration

Website and Domain Migration does not end when rankings stabilize. Long-term SEO success depends on ongoing optimization, monitoring, and maintenance.
Google evaluates websites over time using E-E-A-T principles, which include experience, expertise, authority, and trust. A well-executed migration supports these signals by maintaining technical clarity and content quality.
Regular audits, security updates, and performance improvements reinforce stability. Websites that treat migration as a growth opportunity often see improved rankings once signals settle.
Long-term stability comes from discipline, not shortcuts.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How long does Website and Domain Migration take?
Migration timelines vary, but search engines typically stabilize rankings within a few weeks when best practices are followed.
Q2. Will I lose rankings after migration?
Temporary fluctuations are normal, but long-term losses occur only if SEO best practices are ignored.
Q3. Are 301 redirects mandatory?
Yes, [301 redirects] are essential for preserving ranking signals.
Q4. Should I migrate during peak traffic periods?
No. Google recommends migrating during low-traffic windows.
Q5. Is HTTPS migration separate from domain migration?
It can be combined, but requires careful planning due to security implications.
Q6. How do I track migration issues?
Use [Google Search Console] and analytics tools.
Q7. What happens to backlinks after migration?
Backlinks transfer authority when redirects are correctly implemented.
Q8. Can migration affect website security?
Yes. Poor server configuration can expose vulnerabilities.
Q9. Should content be changed during migration?
Major content changes should be avoided until rankings stabilize.
Q10. When should I expect full SEO recovery?
Recovery typically occurs within 4–8 weeks for properly executed migrations.
Common Website and Domain Migration Mistakes
- Skipping redirect mapping – Causes ranking loss and broken pages
- Blocking crawlers accidentally – Leads to de-indexing
- Changing URLs unnecessarily – Disrupts authority signals
- Ignoring HTTPS setup – Reduces trust and security
- Failing to monitor data – Delays issue detection
Each of these mistakes directly conflicts with Google best practices and often results in long-term SEO damage.
Conclusion
Website and Domain Migration is not just a technical task—it is a strategic SEO operation that determines long-term visibility and trust. When executed correctly, migration preserves rankings, protects users, and strengthens authority.
At FixHackedSite, we approach migrations with a security-first, SEO-aligned methodology that follows Google standards and industry best practices. A disciplined migration process ensures continuity, stability, and sustainable growth.